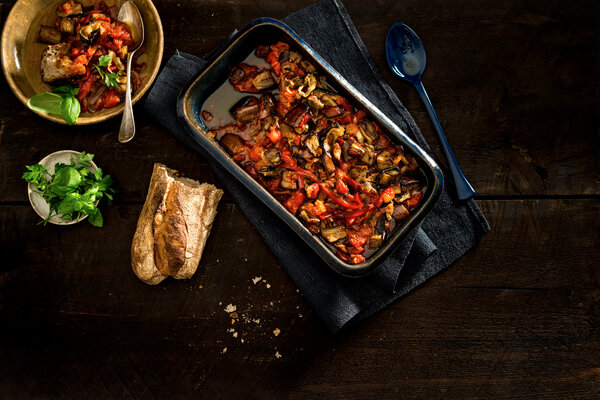
The traditional French dish is a classic for a reason. Melissa Clark will run you through its history, the equipment to use and making the perfect version.

Francesco Tonelli for The New York Times
[This article was originally published on Feb. 14, 2017.]
The French have a genius for cooking with vegetables. Even the humblest onion is transformed into something glorious in the hands of a Gallic cook. Ratatouille, one of jewels of Provençal cooking, is a fine example of that tradition. This guide is part of The New Essentials of French Cooking, the 10 definitive dishes every modern cook should master.
Vegetables are the bedrock of French cuisine, the foundation upon which all is built. Although cooking bibles like “The Escoffier Cookbook” and “Larousse Gastronomique” may not have as many recipes centering on artichokes and carrots as they do on chicken or beef, it is only because vegetables suffuse the canon and the kitchen, from the broths and sauces that serve as the base of elaborate dishes, to the garnishes that finish them.
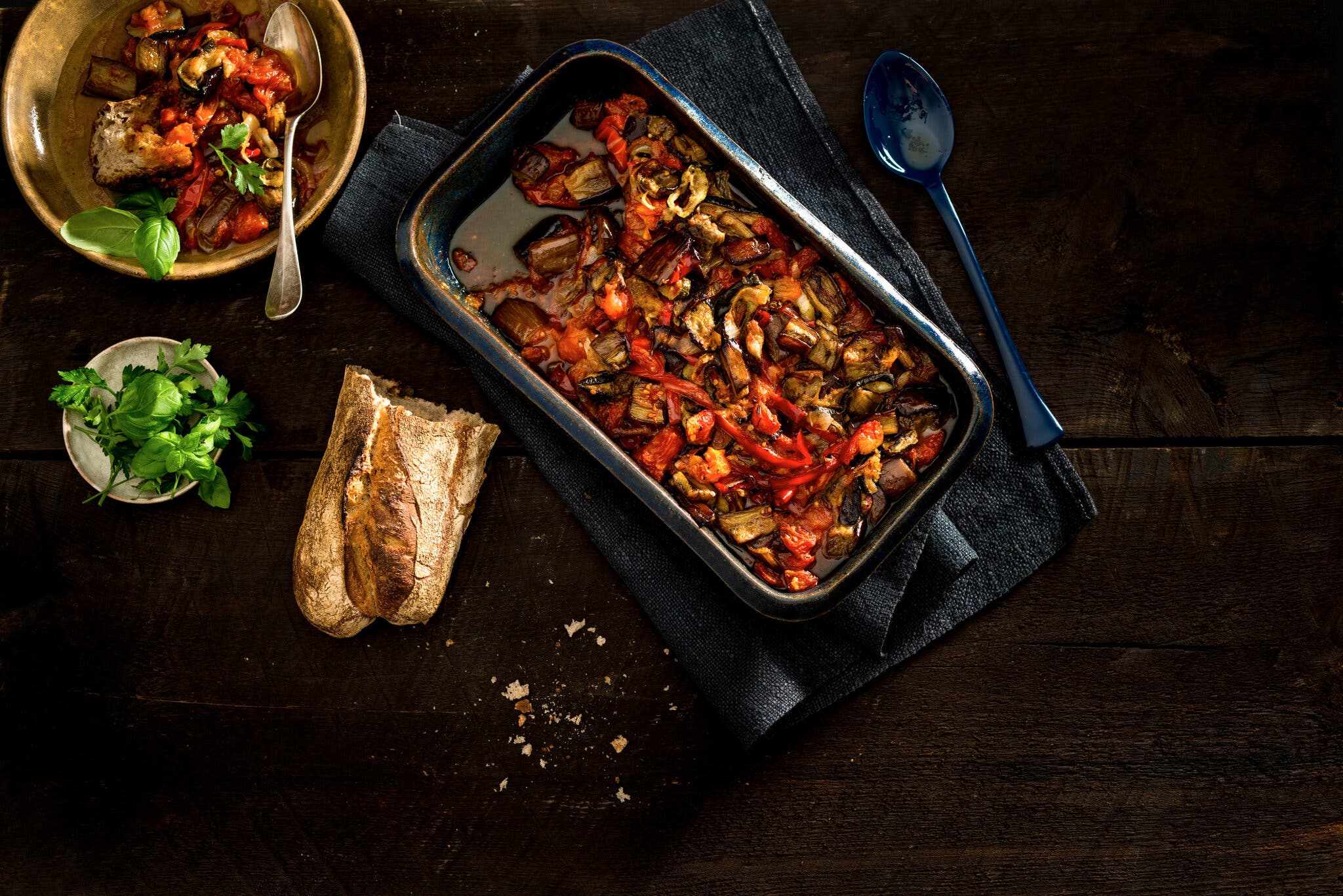
But there are a handful of dishes where vegetables are the stars. Ratatouille is beloved for its silky, olive oil-imbued vegetables, which are saturated with the summery scents of garlic and herbs. By mastering it, you will gain not only deeper insights into how to cook the vegetables in the recipe, but you will also be able to apply that knowledge to other vegetables, making you a better cook all around.

Francesco Tonelli for The New York Times
Unlike much of French cuisine, ratatouille does not have a set recipe or precise technique. There are as many versions as there are cooks, each slightly different in method and ingredients.
The most traditional recipes call for cooking each vegetable separately in a pot on the stove until well browned, layering everything back into the pot with a generous amount of olive oil and some tomatoes, and then letting it all slowly stew. Most cooks agree that this is the best way to ensure that the vegetables are cooked to perfection before all are combined, and the flavors left to meld.
However, all that standing at the stove stirring vegetables can become tedious. Even “Larousse Gastronomique” discards that method in its official recipe, throwing everything into the same pan in stages without the benefit of that individual browning.
But there is another, better way around the tedium: using your oven. This is what many contemporary French cooks do, and it’s the method on which our recipe is based. All the vegetables are bathed in olive oil and roasted separately on baking pans until well browned. Then they’re mixed together in one pan, covered with more oil and some tomato, and cooked again until everything condenses in flavor and practically falls apart, soaking up the good oil and tomato almost like a confit.
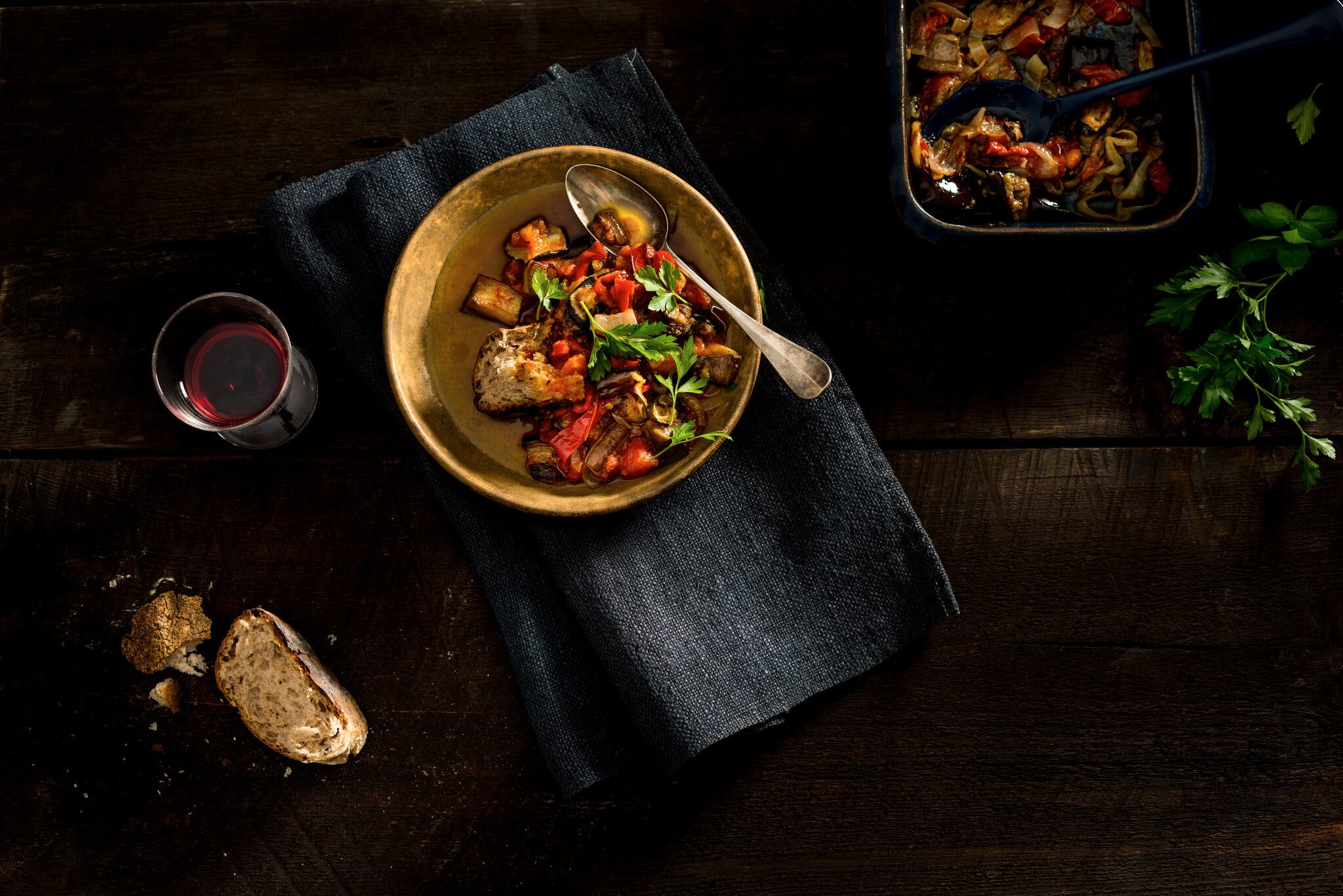
That time spent steeping in good oil makes ratatouille one of the rare vegetable dishes that improves as it sits. It is best made in advance, and you can be flexible with the way you cook it, roasting the vegetables in stages as time allows, then combining them all even days later. It is also wonderfully versatile at the table, making a fine starter, side dish or main course, one that can be eaten warm, at room temperature or cold.
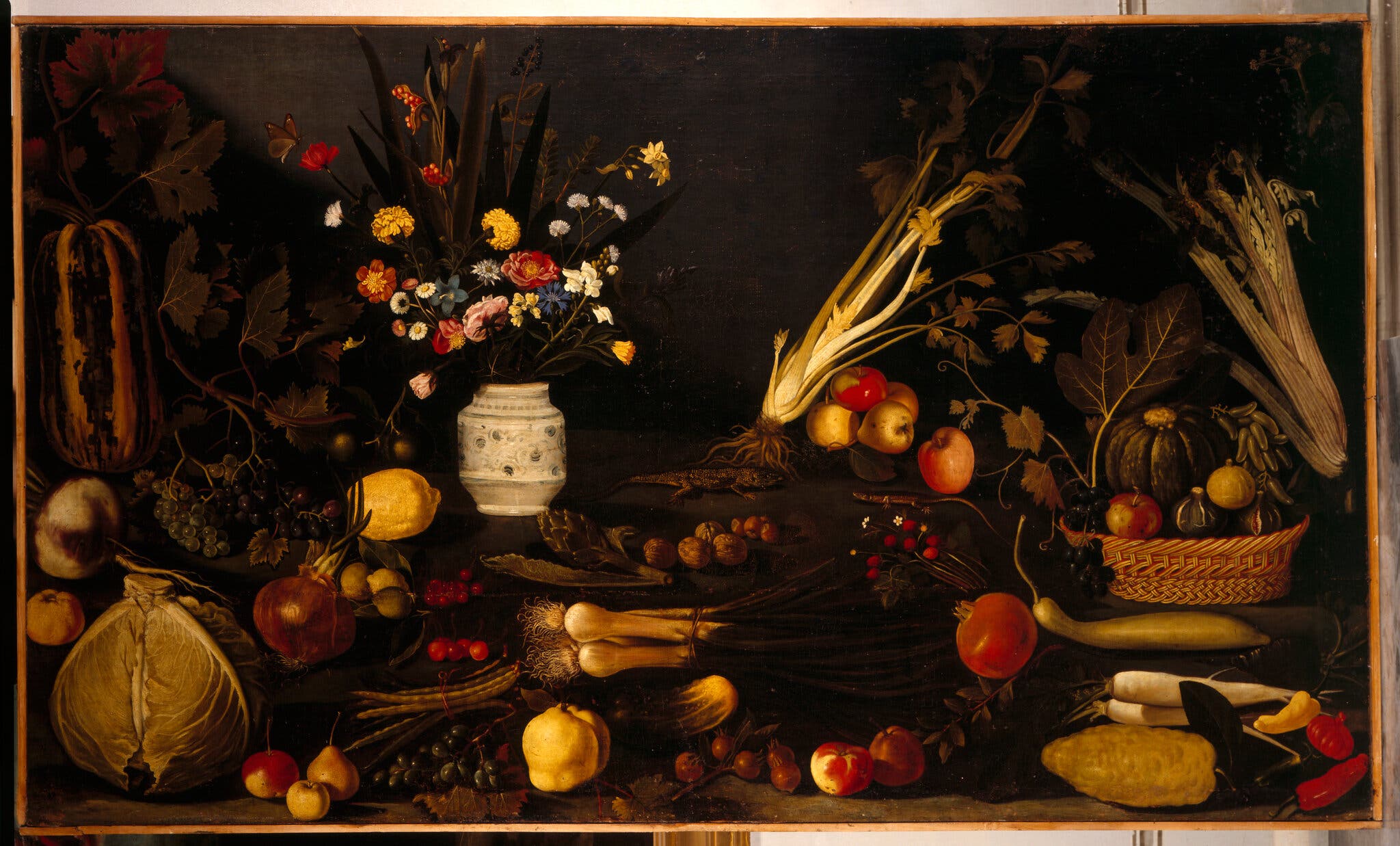

“Still Life With Flowers and Vegetables” by Caravaggio (1571-1610).Nimatallah / Art Resource, NY
A slowly cooked stew of eggplant, onions, peppers, summer squash and tomatoes has been simmering on hearths around the Mediterranean since the 16th century, when tomatoes, peppers and squash from the Americas met the eggplant, onion and olive oil already in residence.
This basic combination of summer vegetables takes different forms throughout the region. In Catalonia, it is simmered until it is almost jamlike and called samfaina. In Turkey, it is known as turlu and may also contain potatoes, okra and green beans. Lebanon, Egypt and Greece all have versions. In Provençe, it is scented with herbs and garlic and called ratatouille.
The term, which came into use in the 19th century, is derived from the French verbs ratouiller and tatouiller, both meaning to stir up. And the pleasing, percussive-sounding word captures the essence of this dish: a stirring of several vegetables that have been cooked separately before being combined.
Originally, a ratatouille could be any kind of simple or coarse stew. It could include meat, or it could do without it. Nineteenth-century French military slang referred to the dish as a “rata.” The first written mentions of the all-vegetable stew from Nice that we know today, also called sauté à la Niçoise, came in the early 20th century.
But by 1930, ratatouille had become entrenched in the Provençal repertoire. Henri Heyraud, the author of “La Cuisine à Nice,” described it as a ragoût of eggplant, zucchini, peppers and tomatoes. The use of the word ragoût here is fitting; it means to revive the taste, which is exactly what ratatouille does, giving cooked vegetables and herbs new verve when they are combined and cooked again.
As Provençal cuisine became fashionable all over France (and to a lesser degree in Britain and the United States) in the latter part of the 20th century, the popularity of ratatouille grew. It has since become a summer staple to serve with simple grilled meats, or as a main course in its own right, with the requisite bottle of rosé.
Sharp knives
You need a chef’s knife and paring knife to prepare the vegetables. And a well-sharpened knife will make all that chopping go noticeably faster than a dull knife.
Baking sheets
The vegetables in this ratatouille are roasted individually before they are all combined. Ideally, you will have at least four large rimmed metal baking sheets for doing so. You can get away with fewer, but you will need to cook the vegetables in batches.
Large baking dish
You could heap all of the vegetables onto a baking sheet when it is time to cook them together. But a large, shallow, attractive casserole that can travel straight to the table is an appealing way to serve the dish.
Ratatouille is a freer and easier recipe than much of what you’ll find in the canon of French cuisine, requiring you to spend more time choosing the ingredients than actually fiddling with them. That said, there are some techniques that will help you get the most deeply flavored dish.
Blanching and Peeling the Tomatoes
Blanching and peeling tomatoes for ratatouille.By Meg Felling
Blanching tomatoes helps loosen the skin, making them easier to peel without losing any of their precious, sweet juices. The trick is remove them from the boiling water before their flesh is cooked. You want to cook only the skin.
Choose tomatoes that are ripe but still firm; soft tomatoes won’t hold up to the peeling and blanching. You can use any variety as long as it is flavorful and sweet. However, using large round tomatoes rather than small plum tomatoes makes the blanching, peeling and seeding go more quickly.
To begin, bring a medium pot of water to a boil. One at a time, drop the whole tomatoes into the boiling water. Cover and let boil for 10 seconds. Using a slotted spoon or tongs, immediately remove the tomatoes from the pot and plunge them into a bowl of ice water to stop the cooking. Hold a cooled tomato in your hand and use a small paring knife to cut out the stem. From there, you can start to peel the skin. It should slip right off.
Cut the peeled tomato in half around its equator. Set up a bowl with a mesh sieve sitting on top. Squeeze the tomato halves over the sieve so the seeds are caught in the mesh and the juices pool in the bowl. The seeds should slip out easily, but you can use your fingers to pry any stubborn ones from the tomato flesh. Discard the seeds in the sieve. Dice the tomato pulp and add it to the bowl with their juices. Repeat peeling and seeding with the remaining tomatoes.

Francesco Tonelli for The New York Times
Cooking and Serving
-
When you are making ratatouille, the quality of the olive oil is as important as that of the vegetables. Make sure to choose a good extra-virgin oil, preferably from France. You’ll be using a lot of it here.
-
If you don’t have four baking sheets, roast the vegetables on individual sheets in succession. Transfer the cooked vegetables to a bowl as they finish cooking. This takes longer, since you can’t roast all the vegetables at once. (Likewise, if you can’t fit all of the baking sheets into your oven at once, cook them in batches.)
-
If your ratatouille emerges from the oven with a lot of excess liquid in the pan, pour the liquid into a saucepan and reduce it over the stove. Then add it back to the dish once it is reduced, to take advantage of its flavor.
Try the traditional method
Instead of roasting each vegetable on baking sheets, cook them on the stovetop. Heat your largest skillet on the stove, adding a film of oil, and cook each vegetable separately (and the onions, smashed garlic and herbs together). Cook in batches if necessary, so as not to crowd the pan. (If you crowd the pan, the vegetables will steam rather than brown, and cook unevenly.) As the vegetables soften and brown, transfer them to a bowl. (You can add all the different kinds of cooked vegetables to the same bowl.) Add more oil with each batch of vegetables, and season with salt and pepper as you go. When all of the vegetables are cooked, transfer them back to the skillet, along with the tomatoes, grated garlic and a good dose of olive oil. Simmer, uncovered, until they meld together, about 30 to 45 minutes.
You can make this dish in stages, if that suits your schedule. Roast the vegetables separately a day or two before combining them, and then refrigerate them. When you are ready to return to them, combine with the tomatoes, remaining herbs and oil and cook for at least an hour to finish.
Or make the entire dish ahead.
It is best to make your ratatouille one or two days before serving so the flavors have a chance to meld and mellow. Once the dish is cooked and cooled, transfer it to a container, adding a little oil if necessary, and refrigerate for up to five days. When you’re ready to serve, bring it to room temperature (this takes about an hour) and drizzle with a tiny bit more olive oil. You can also reheat it on the stove or in the microwave to serve it warm.